The efficacy of Osimertinib was demonstrated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (ADAURA [NCT02511106]) for the adjuvant treatment of patients with EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutation-positive NSCLC who had complete tumor resection, with or without prior adjuvant chemotherapy. Eligible patients with resectable tumors (stage IB – IIIA according to American Joint Commission on Cancer [AJCC] 7th edition) were required to have predominantly non-squamous histology and EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutations identified prospectively from tumor tissue in a central laboratory by the cobas® EGFR Mutation Test. Patients with clinically significant uncontrolled cardiac disease, prior history of ILD/pneumonitis, or who received treatment with any EGFR kinase inhibitor were not eligible for the study.
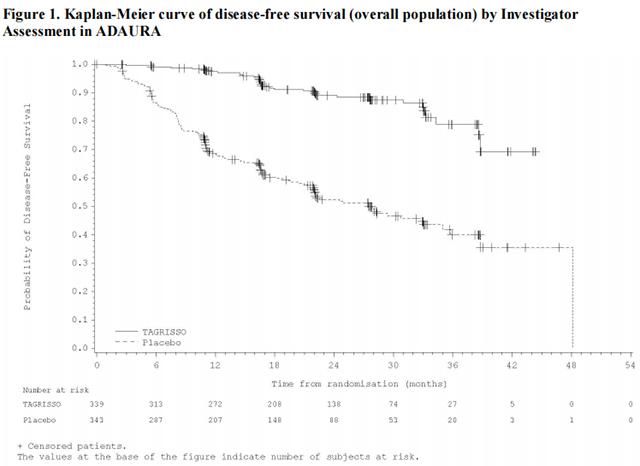
ADAURA demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful difference in DFS for patients treated with Osimertinib compared to patients treated with placebo. Overall survival (OS) data were not mature at the time of the DFS analysis with 27% of the 94 deaths required for the final analysis of OS in patients with stage II-IIIA disease. Efficacy results from ADAURA are summarized in Table 8 and Figure 1, respectively.
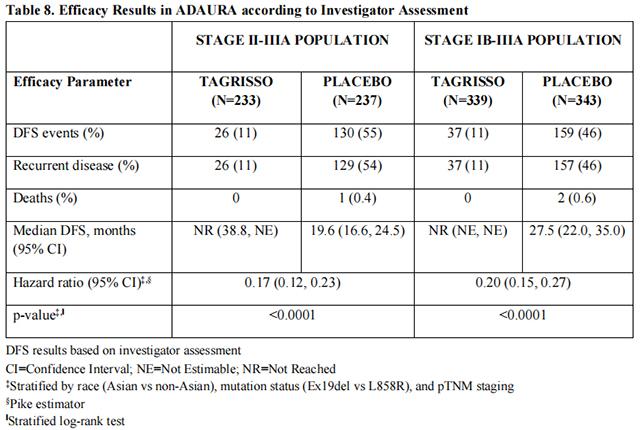
In an exploratory analysis of site(s) of relapse, the proportion of patients with CNS involvement at the time of disease recurrence was 5 patients (1.5%) on the Osimertinib arm and 34 patients (10%) on the placebo arm.
The efficacy of Osimertinib was demonstrated in a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, active-controlled trial (FLAURA [NCT02296125]) in patients with EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutation-positive, metastatic NSCLC, who had not received previous systemic treatment for metastatic disease. Patients were required to have measurable disease per RECIST v1.1, a WHO performance status of 0-1, and EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutation in tumor prospectively identified by the cobas® EGFR Mutation Test in a central laboratory or by an investigational assay at a CLIA-certified or accredited laboratory. Patients with CNS metastases not requiring steroids and with stable neurologic status for at least two weeks after completion of definitive surgery or radiotherapy were eligible. Patients were assessed at the investigator’s discretion for CNS metastases if they had a history of, or suspected, CNS metastases at study entry.
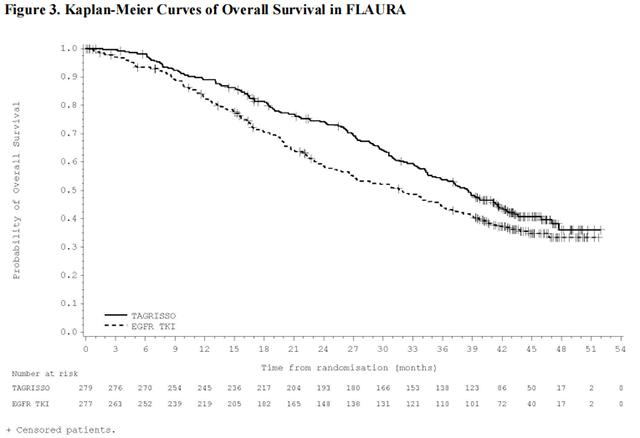
FLAURA demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS for patients randomized to Osimertinib as compared to erlotinib or gefitinib (see Table 9 and Figure 2). The final analysis of overall survival demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in overall survival in patients randomized to Osimertinib compared to erlotinib or gefitinib. (see Table 9 and Figure 3).
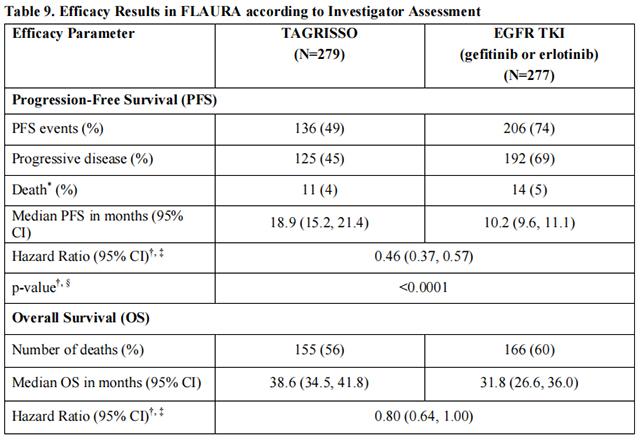
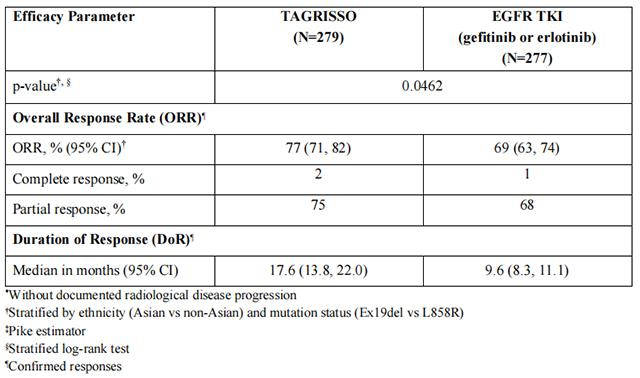
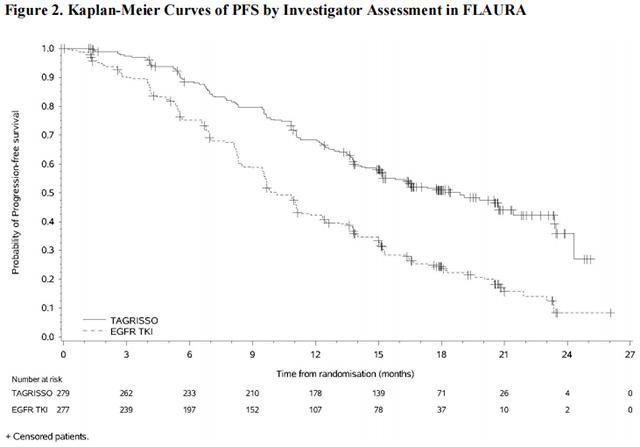
In a supportive analysis of PFS according to blinded independent central review, median PFS was 17.7 months in the Osimertinib arm compared to 9.7 months in the EGFR TKI comparator arm (HR=0.45; 95% CI: 0.36, 0.57).
Of 556 patients, 200 patients (36%) had baseline brain scans reviewed by BICR; this included 106 patients in the Osimertinib arm and 94 patients in the investigator choice of EGFR TKI arm. Of these 200 patients, 41 had measurable CNS lesions per RECIST v1.1. Results of pre-specified exploratory analyses of CNS ORR and DoR by BICR in the subset of patients with measurable CNS lesions at baseline are summarized in Table 10.
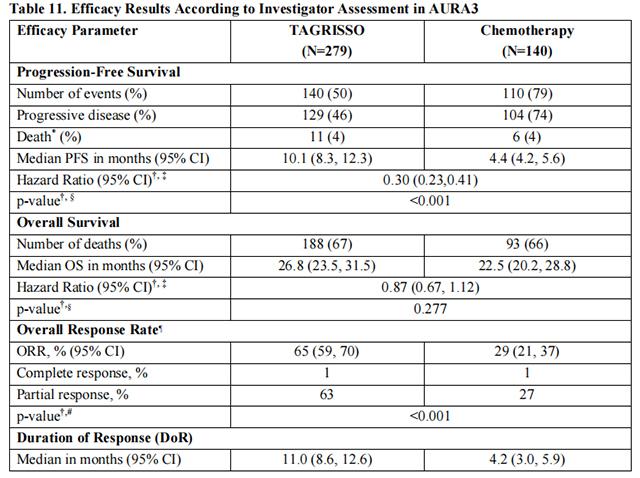
The efficacy of Osimertinib was demonstrated in a randomized, multicenter open-label, active-controlled trial in patients with metastatic EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC who had progressed on prior systemic therapy, including an EGFR TKI (AURA3). All patients were required to have EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC identified by the cobas® EGFR Mutation Test performed in a central laboratory prior to randomization.
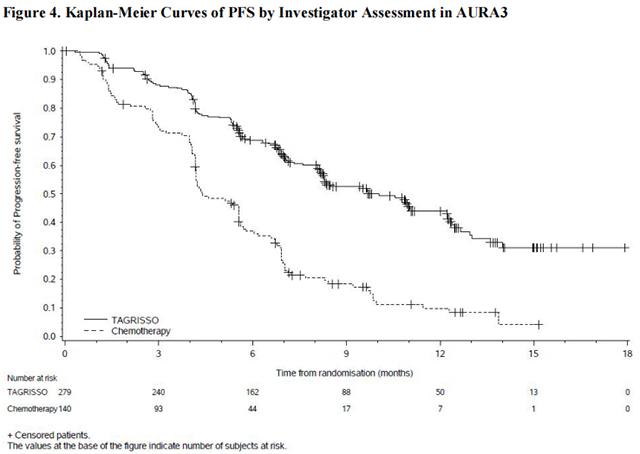
In AURA3, there was a statistically significant improvement in PFS in the patients randomized to Osimertinib compared to chemotherapy (see Table 11 and Figure 4). No statistically significant difference was observed between the treatment arms at final OS analysis. At the time of the final OS analysis, 99 patients (71%) randomized to chemotherapy had crossed over to Osimertinib treatment.
from FDA,2022.10
Does osimertinib workFor patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer, the ···【more】
Release date:2025-03-06Recommended:217
As an important drug for targeted therapy of lung cancer, osimertinib has attrac···【more】
Release date:2025-03-06Recommended:279
To investigate the performance of osimertinib in the treatment of lung cancer an···【more】
Release date:2025-03-05Recommended:258