The efficacy of Gilteritinib was assessed in the ADMIRAL Trial (NCT02421939), which included adult patients with relapsed or refractory AML having a FLT3 ITD, D835, or I836 mutation by the LeukoStrat® CDx FLT3 Mutation Assay. Gilteritinib was given orally at a starting dose of 120 mg daily until unacceptable toxicity or lack of clinical benefit.
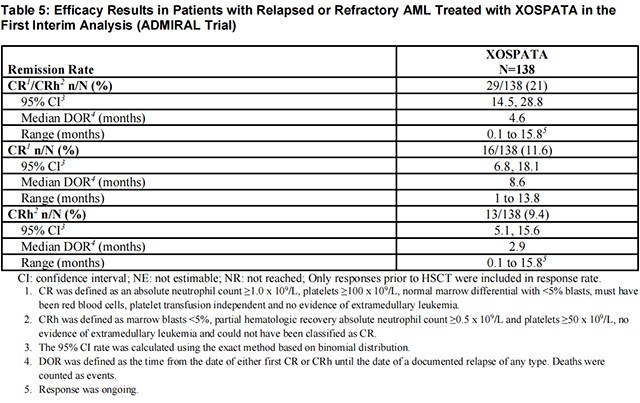
The efficacy of Gilteritinib was established on the basis of the rate of complete remission (CR)/CR with partial hematological recovery (CRh), the duration of CR/CRh (DOR), and the rate of conversion from transfusion dependence to transfusion independence at the first interim analysis in the ADMIRAL trial (n=138). The median follow-up was 4.6 months (95% CI: 2.8, 15.8). Fourteen patients were still in remission at the time of the first interim DOR analysis. The efficacy results are shown in Table 5. For patients who achieved a CR/CRh, the median time to first response was 3.6 months (range, 0.9 to 9.6 months). The CR/CRh rate was 29 of 126 in patients with FLT3-ITD or FLT3-ITD/TKD and 0 of 12 in patients with FLT3-TKD only.
Among the 106 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 33 (31.1%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post-baseline period. For the 32 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 17 (53.1%) remained transfusion-independent during any 56-day post-baseline period.
The final analysis of the ADMIRAL trial included 371 adult patients randomized 2:1 to receive Gilteritinib 120 mg once daily (n=247) over continuous 28-day cycles or a prespecified chemotherapy regimen (n=124). Randomization was stratified by response to first-line AML therapy and prespecified chemotherapy. The prespecified chemotherapy regimens included high intensity combinations (MEC and FLAG-IDA) and low intensity regimens (LDAC and AZA).
FDA,2022.01
This study aims to investigate the safety and efficacy of the combination of gil···【more】
Release date:2024-11-22Recommended:285