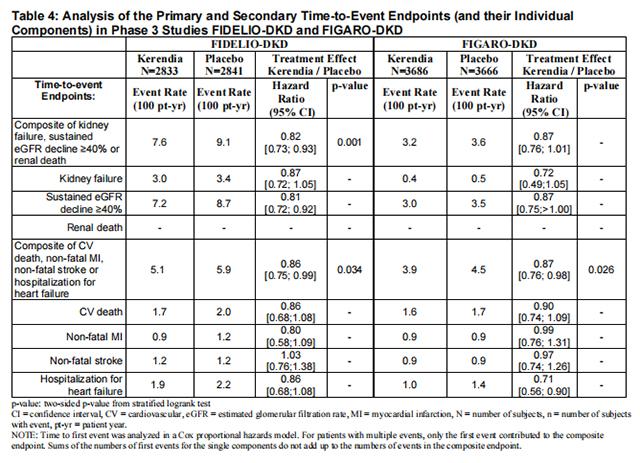
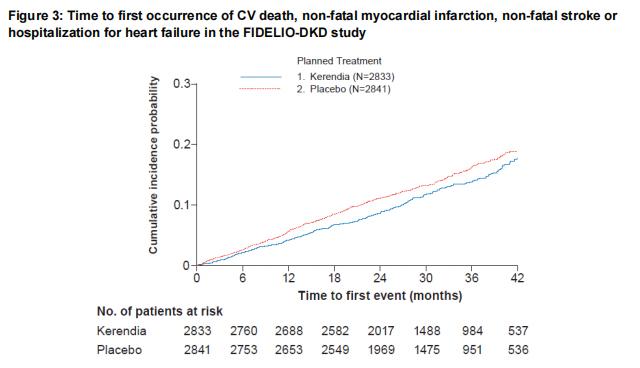
In FIDELIO-DKD, Finerenone reduced the incidence of the primary composite endpoint of a sustained decline in eGFR of ≥ 40%, kidney failure, or renal death (HR 0.82, 95% CI 0.73-0.93, p=0.001) as shown in Table 4 and Figure 1. The treatment effect reflected a reduction in a sustained decline in eGFR of ≥ 40% and progression to kidney failure. There were few renal deaths during the trial. Finerenone also reduced the incidence of the secondary composite endpoint of cardiovascular (CV) death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), non-fatal stroke or hospitalization for heart failure (HR 0.86, 95% CI 0.75-0.99, p=0.034) as shown in Table 4 and Figure 3. The treatment effect reflected a reduction in CV death, non-fatal MI, and hospitalization for heart failure. The treatment effect on the primary and secondary composite endpoints was generally consistent across subgroups.
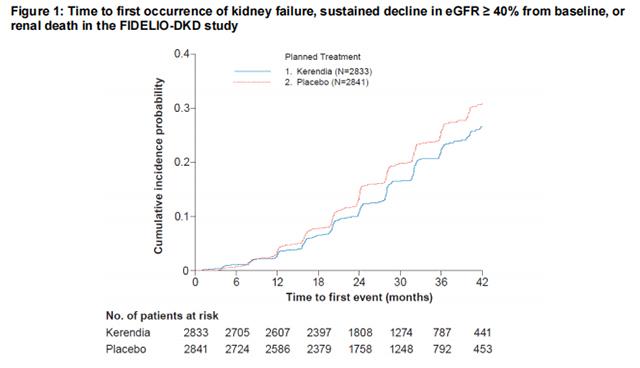
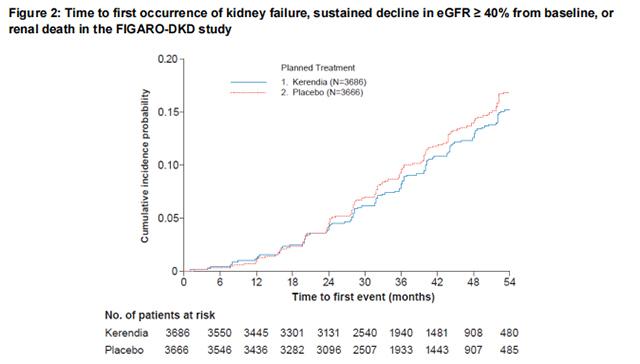
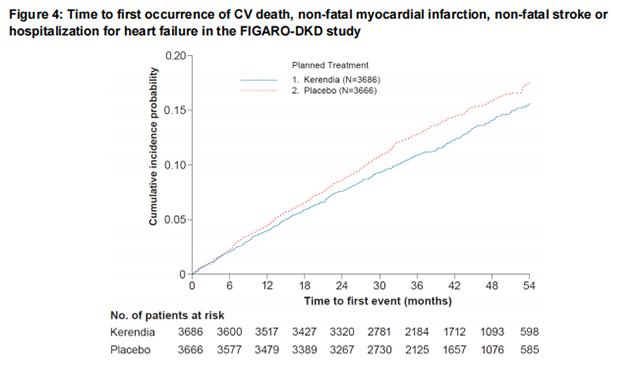
In FIGARO-DKD, Finerenone reduced the incidence of the primary composite endpoint of CV death, non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke or hospitalization for heart failure (HR 0.87, 95% CI 0.76-0.98, p = 0.026) as shown in Table 4 and Figure 4. The treatment effect was mainly driven by an effect on hospitalization for heart failure, though CV death also contributed to the treatment effect. The treatment effect on the primary composite endpoint was generally consistent across subgroups, including patients with and without pre-existing cardiovascular disease. The findings for the renal composite endpoint are shown in Table 4 and Figure 2.
来自FDA,2022.09
Focusing on the clinical value of finerenone, the medical community is conductin···【more】
Release date:2025-04-18Recommended:240
The medical community is always exploring new treatment options, and this articl···【more】
Release date:2025-04-18Recommended:300
The new drug finerenone has attracted widespread attention in the field of chron···【more】
Release date:2025-04-17Recommended:211